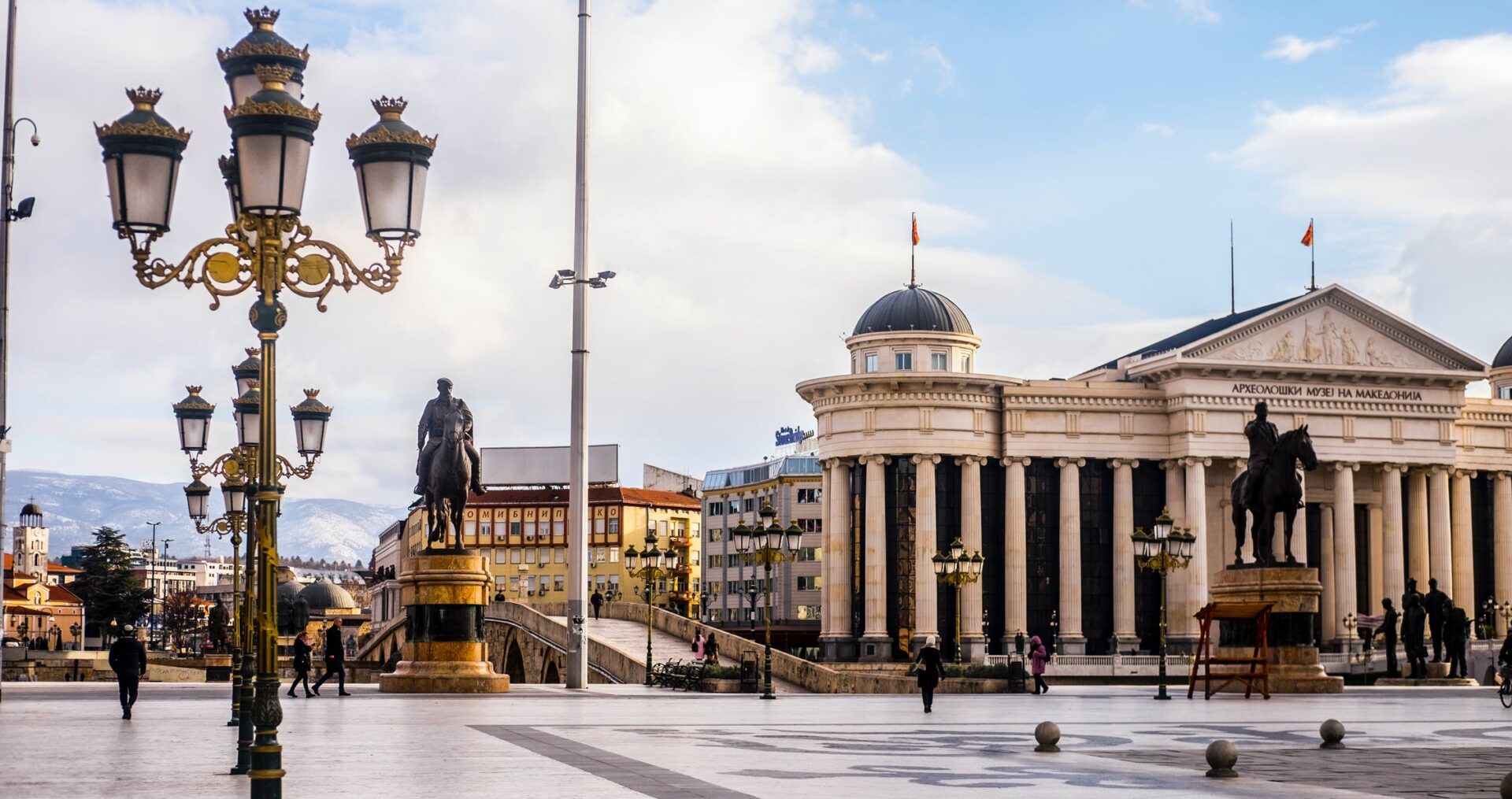
Yugoslavia is liked to be compared to the Soviet Union, and its collapse to the collapse of the USSR. I will take this comparison as a basis and briefly describe the main peoples of the former Yugoslavia by analogy with the peoples of the former Union.
SOUTHERN SLAVIA, a state that existed in 1918-1992 in southeastern Europe, in the northwestern and central part of the Balkan Peninsula.
Yugoslavia was, by socialist standards, a very developed country. It had the highest standard of living among the socialist countries, not counting the GDR. In Russia, the older generation may still remember that a trip to Yugoslavia was almost equal to a trip to a capitalist country.
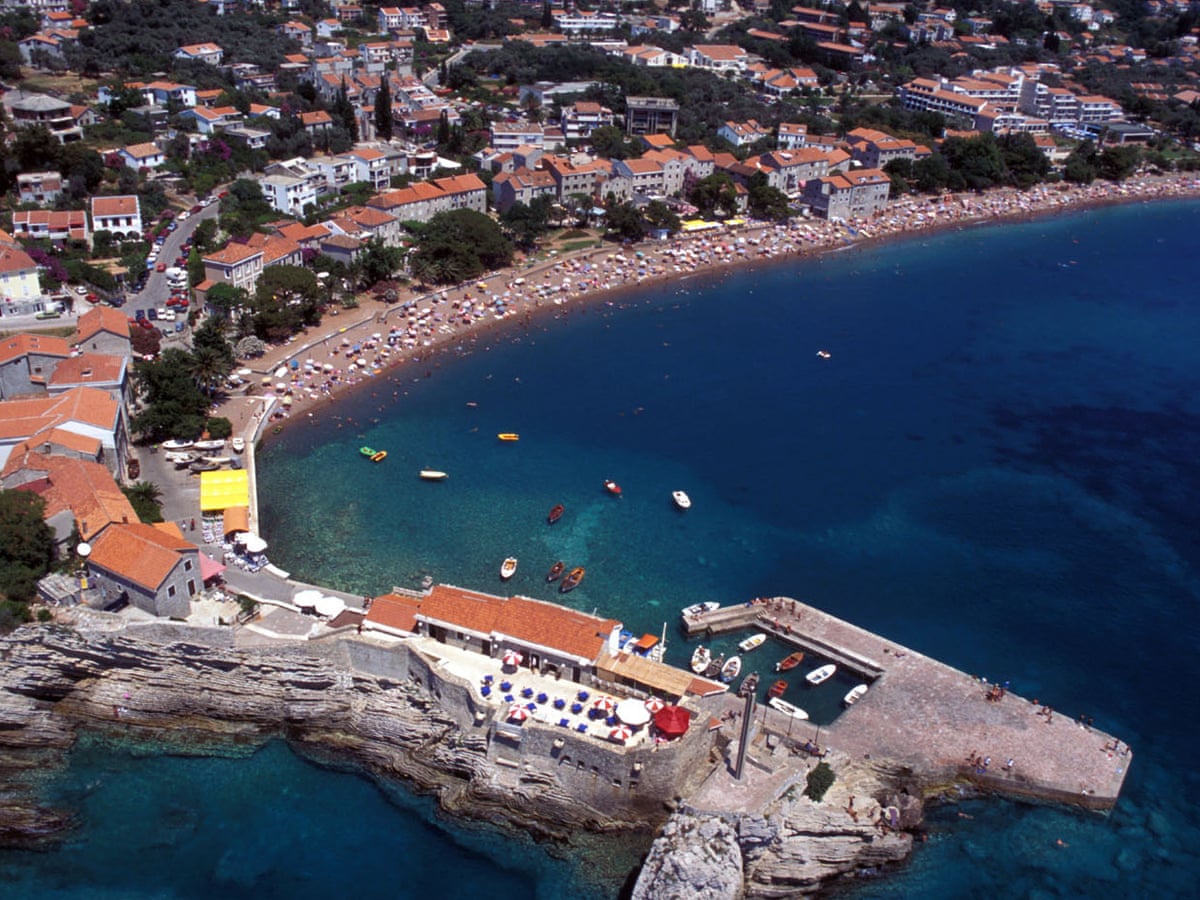

Then, in the early 1990s, there was war, economic recession, and unemployment. Therefore, many people still treat the socialist past normally and even with nostalgia. It is clear that socialism is remembered more warmly in less developed countries (Bosnia, Serbia, etc.), while in more developed countries (Slovenia and Croatia) it is rather viewed negatively.
A characteristic feature – almost everywhere in the former Yugoslavia is very clean. In towns, like in our country, there is no dirt or dust on various surfaces. You can almost always sit down on the curb or steps without having to worry about the cleanliness of your pants. From passing cars do not rise clouds of dust, and on country roads there is no dirty curb, so you can safely put your backpack when you catch the car.
Josip Broz Tito – Yugoslav political, state and military figure, Marshal of Yugoslavia, People’s Hero of Yugoslavia, president of SFRY (before 1963), from 1939 – General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia (CPY) (from 1952 – Union of Communists of Yugoslavia (UCY), one of the founders of the Nonaligned Movement.
Somthing Interesting About History
Posts
- From the Dinar to Digital Wallets: The Evolution of Payments in the Balkans
 Payment systems in the Balkans have changed completely. When you look at the past three decades, the transformation is dramatic. In the 1990s, there was a period of hyperinflation. Currencies were unstable. People did not trust banks. Now there is a sophisticated digital infrastructure. In some areas, it rivals Western Europe. In others, it goes…
Payment systems in the Balkans have changed completely. When you look at the past three decades, the transformation is dramatic. In the 1990s, there was a period of hyperinflation. Currencies were unstable. People did not trust banks. Now there is a sophisticated digital infrastructure. In some areas, it rivals Western Europe. In others, it goes… - Retrofuturism of Yugoslavia: Forgotten Architectural Utopias of the Balkans
 Most of us tend to forget some of the craziest chapters in architectural history, for a few short decades after World War II, a country that no longer exists managed to build some of the most astonishing concrete structures the world has ever seen. Yugoslavia, stuck between East and West from 1948 until about 1980,…
Most of us tend to forget some of the craziest chapters in architectural history, for a few short decades after World War II, a country that no longer exists managed to build some of the most astonishing concrete structures the world has ever seen. Yugoslavia, stuck between East and West from 1948 until about 1980,… - Does Yugoslavia Still Exist in Modern Europe?
 Cryptocurrency has long ceased to be exclusively a tool for investors and traders. While a few years ago it was associated only with bitcoin and quick money on the stock exchange, today the scope of application of digital assets is much wider. One of the areas where cryptocurrency and blockchain are beginning to play an…
Cryptocurrency has long ceased to be exclusively a tool for investors and traders. While a few years ago it was associated only with bitcoin and quick money on the stock exchange, today the scope of application of digital assets is much wider. One of the areas where cryptocurrency and blockchain are beginning to play an…
15 interesting facts about Yugoslavia
- Yugoslavia was a European state that existed on the Balkan Peninsula between 1918 and 2003.
- After the collapse of Austria-Hungary in 1918, the lands of Croatia, Slovenia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Dalmatia, Serbia, and Montenegro were united into the – Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (KCS).
- The monetary unit of the country was the Yugoslav dinar.
- Until 1945, the monarchic form of government operated in Yugoslavia, which was replaced by the republican system.
- During World War II (1939-1945) Yugoslavia fought against Germany and its allies.
- An interesting fact is that during World War II, the largest guerrilla movement after the Soviet Union operated in the country.
- Since 1947, Yugoslavia was a federative state of 6 equal republics: Croatia, Slovenia, Serbia, Montenegro, Macedonia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina.
- Did you know that in addition to the 6 republics, the country also included two autonomous provinces, Kosovo and Vojvodina?
- Belgrade, the Yugoslav capital, is considered one of the oldest cities in Europe. The first mentions of it date back to the 3rd century B.C.
- Disagreements between the Yugoslav and Soviet leaders, Josip Broz Tito and Stalin, led to a breakdown in diplomatic relations. In 1949 the USSR broke the Treaty of Friendship with Yugoslavia.
- All flags (see Interesting facts about the flag) and coats of arms of the Yugoslav republics had stars on them.
- According to Tito’s will, after his death the office of president was to be eliminated, and the country was to be ruled by a Presidium, whose members would succeed each year.
- In the mid-1980s, Yugoslavia experienced tremendous inflation, accompanied by economic collapse. This led to a confrontation between the economically more developed Serbia, Croatia, and Slovenia with the other republics.
- The official language in Yugoslavia was Serbo-Croat.
- In the midst of the political devastation of 1991, 4 of the 6 republics broke away from Yugoslavia: Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Macedonia. As a result, a military conflict broke out in Slovenia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina between the Yugoslav People’s Army and local rebels.